In the realm of military aviation, ambitious projects often promise revolutionary advancements, only to face challenges that lead to their downfall. The story of the RAH-66 Comanche stands as a testament to the complexities of engineering and the unpredictability of military priorities.
Amid the backdrop of Cold War tensions, the 1980s witnessed the United States grappling with the need for modern reconnaissance and light attack helicopters. The RAH-66 Comanche emerged from the Light Helicopter Experimental (LHX) program, a visionary effort to replace aging helicopter models like the Bell UH-1 Iroquois, Bell AH-1 Cobra, Hughes OH-6 Cayuse, and Bell OH-58 Kiowa. The stakes were high, as the Comanche aimed to excel in armed reconnaissance, light attack, and air combat.
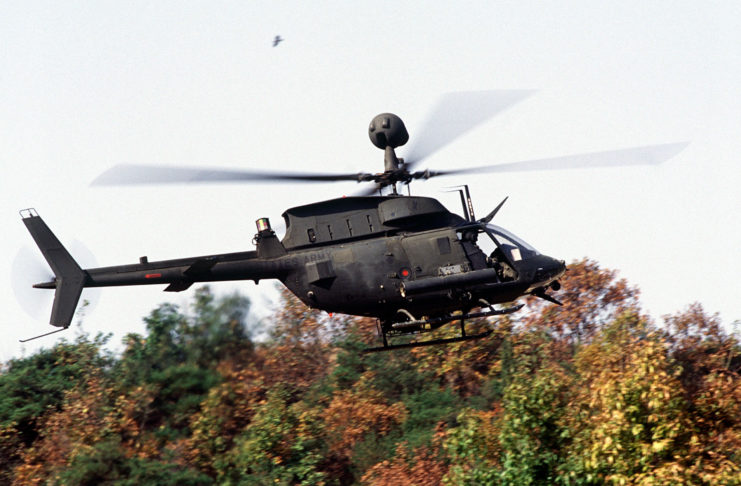

The driving force behind the Comanche’s inception was the perceived threat posed by the Soviet Union. The program’s architects believed that a new generation of helicopters was essential to counter potential Soviet advancements. Boeing-Sikorsky and Bell-McDonnell Douglas were the contenders, but Boeing-Sikorsky secured a substantial $2.8 billion contract to develop six prototypes.
What set the Comanche apart were its groundbreaking features, which borrowed elements from stealth technology. The angular radar-reflecting surfaces inspired by the Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk lent the Comanche an air of invisibility, echoing the famous “You can’t see me” slogan. These design choices aimed to reduce its radar signature and infrared emissions, critical attributes for evading detection.
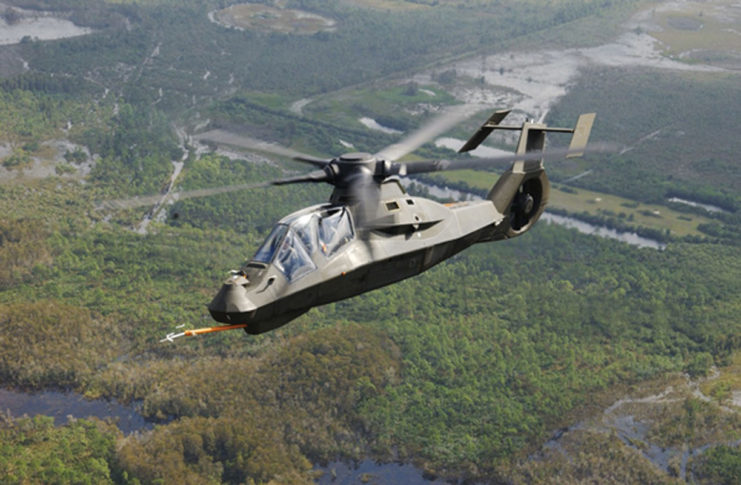

The Comanche prototypes were laden with cutting-edge materials and innovations. Radar-absorbing composite materials graced its surfaces, significantly reducing its radar signature. The careful routing of engine exhaust through the tail section decreased its infrared signature by an impressive 75 percent. Even the rotor blades were armored with graphite plating, capable of withstanding heavy gunfire while generating minimal noise.
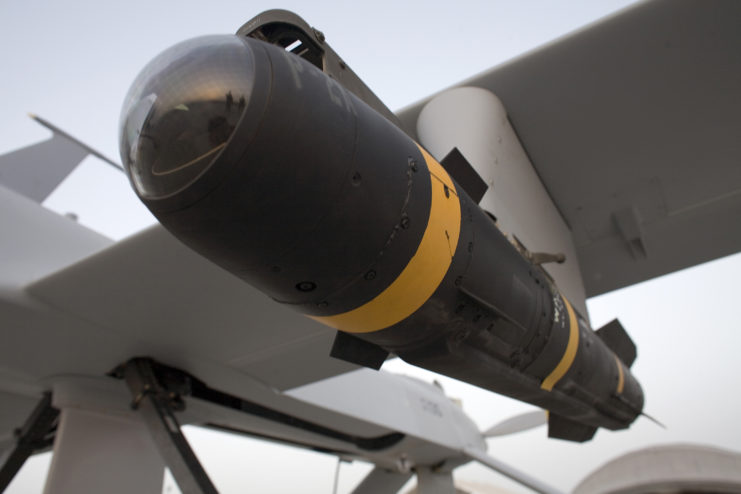

In terms of armament, the Comanche was primed for multifaceted combat scenarios. Internally carried weaponry included a retractable 20-mm XM301 Gatling cannon and space for six AGM-114 Hellfire missiles. An additional eight Hellfire missiles could be mounted externally, along with 12 AIN-92 Stinger air-to-air missiles.
However, despite its promises, the RAH-66 Comanche encountered significant setbacks. Software glitches hindered its performance, leading to less-than-optimal target detection and accuracy. Moreover, efforts to reduce weight proved sluggish, leaving the helicopter’s specifications compromised.
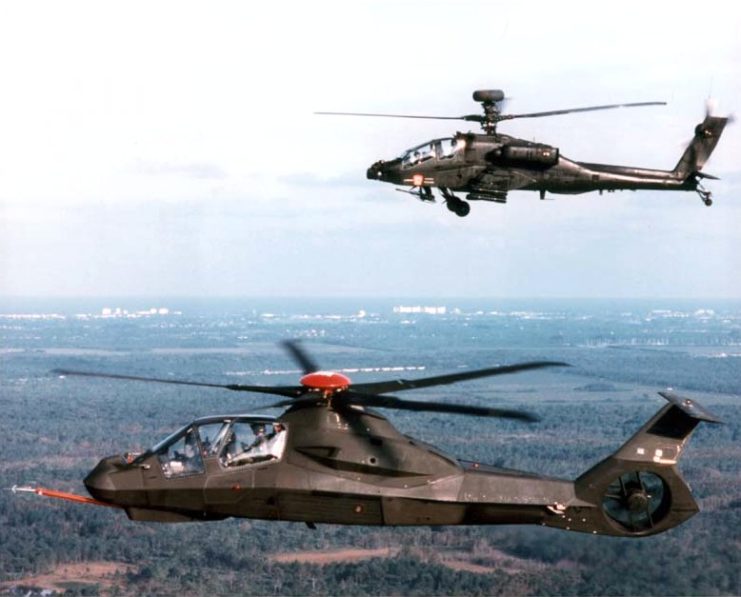

The 9/11 terrorist attacks ushered in a new era of military priorities, prompting a shift away from reconnaissance and light attack platforms. The Comanche’s destiny was sealed, with the US Army reducing its order and ultimately canceling the program two years later.
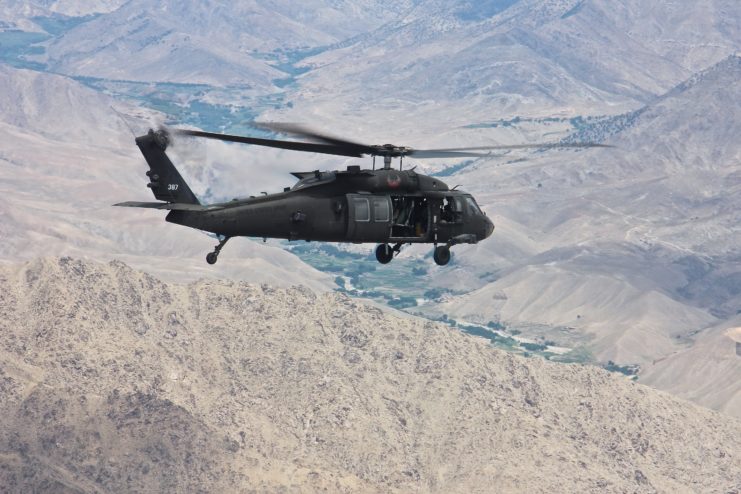
While the Comanche itself never reached its intended heights, its legacy endures. The program yielded invaluable insights that influenced subsequent rotorcraft development. Elements of its design can be glimpsed in later models like the UH-60 Black Hawk, which showcased borrowed innovations like the unconventional tail section. Sikorsky’s S-97 Raider echoes the spirit of the Comanche, proving that the original concept was indeed ahead of its time.

In the annals of military aviation history, the RAH-66 Comanche remains a testament to ambitious aspirations and the challenges inherent in translating them into reality. As technology continues to evolve, the Comanche’s legacy lives on, a reminder that even “failed” projects can pave the way for future successes.