The US F-16 fighter jet is currently one of the world’s most numerous and widespread fixed-wing aircraft and the United States Air Force. On the other hand, the J-10 is the largest fighter aircraft in the Chinese air force in terms of numbers.
Let’s see where their most advanced variants, i.e., F-16v Vs. J10c fighter jets stand their chances against each other.
F-16V
The F-16 fighter is widely recognized as the world’s most successful fourth-generation aircraft. The F-16 fighter has undergone numerous improvements and changes since it was first introduced in the late 1970s. With no fewer than ten derivative models, the overall thrust of the F-110-GE-132 engine has increased by at least roughly 30%.
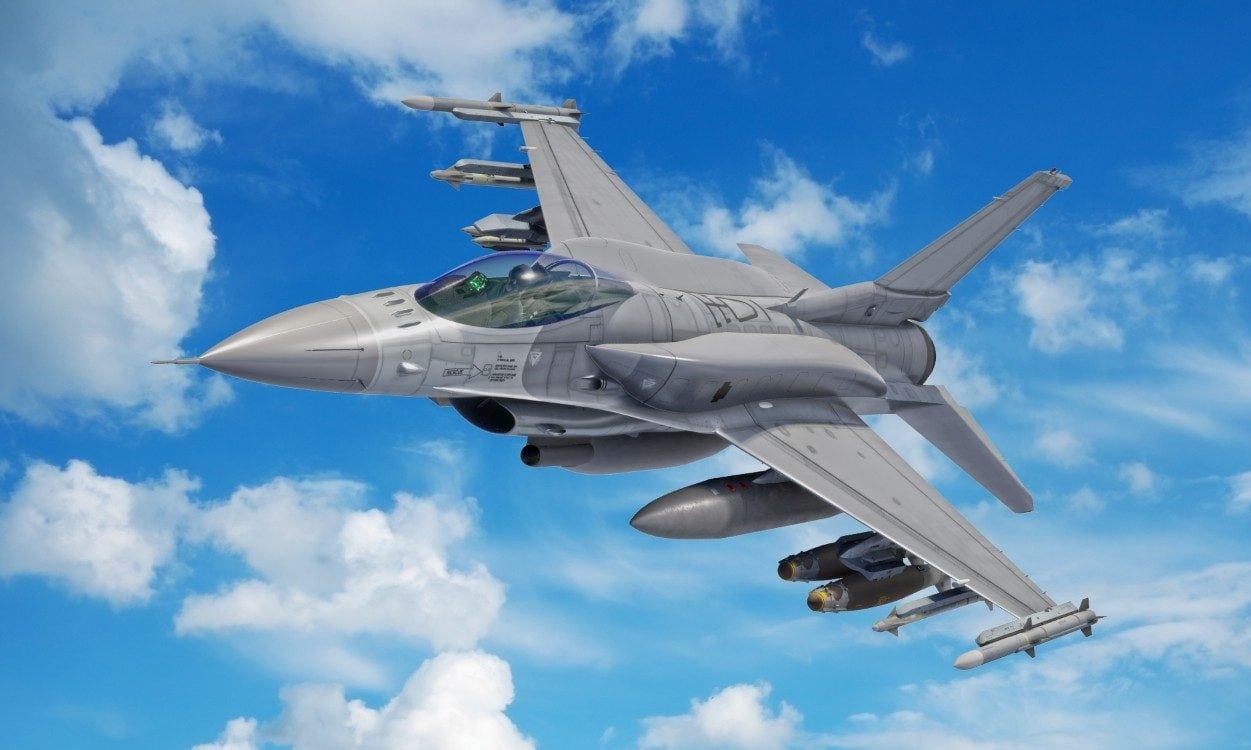

F-16V Viper
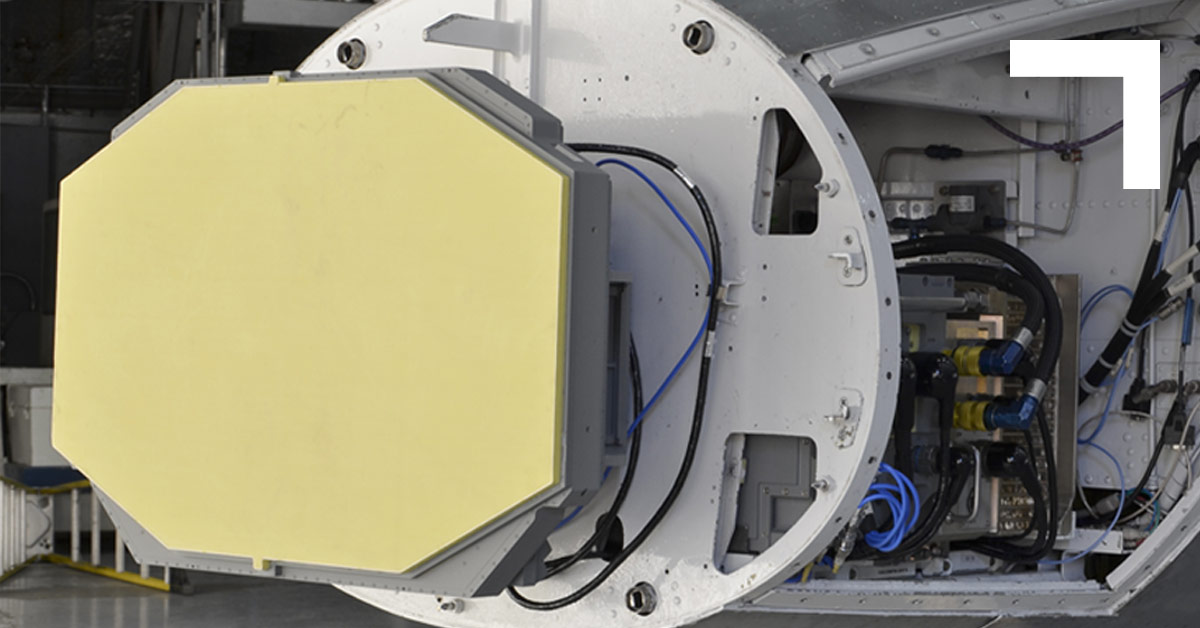
The F-16V is unquestionably a significant advancement over the outdated F-16A/B/C/D variants in terms of capability and capacity to compete in the next-generation battlefield. With the AESA radar upgrade, the F-16V will eventually be able to incorporate the AIM-120D missile with a corresponding 180KM range. The F-16V fighter plane has the same avionics and phased array radar generation as the F35 fighter. Therefore its situational awareness and flexibility are anticipated to be comparable to those of the F35 fighter.
The F-16V has a more durable fuselage and a fire control radar built by Northrop Grumman called the APG-83, which has a flight time of up to 12,000 hours. The fire control radar system and the battle information display system in the cockpit are the essential components of these F-16s. The F-22 and F-35 are the only 5th generation fighters with APG-83 radars.
APG-83 significantly extends the tracking and target detection range of F-16 jets. It has been engineered to resist electronic jamming while also capable of quicker detecting small targets.
To strike enemy radar clusters, the aircraft can optionally be equipped with JDAM bombs or AGM-88 HARM anti-radiation missiles. The central display system in the cockpit is electromechanical equipment created by Elbit Systems. The combat computer on the F-16 Viper has been improved. The aircraft includes a new data-link technology that makes communicating more accessible with advanced aircraft like the F-22 and F-35. The electronic warfare system on the F-16V is also updated. The F-16V Viper is fitted with a Sniper shooting auxiliary device that automatically detects and tracks the target and provides GPS coordinates to guide the vehicle, in addition to having the capacity to carry all of the most advanced missiles and bombs.
The pilot’s helmet-mounted pointing device improves the AIM-9X heat-seeking missile’s combat capabilities. A multi-function display has taken the place of most of the electromechanical components in the cockpit of the F-16V. The aircraft communicates with the F-35 and F-22 using a unique data link controlled by a modern central computer system. The F-16V is regarded by military analysts as one of the world’s leading 4th generation fighters, with combat capabilities comparable to several 4th generation fighter jets because of its open-architecture avionics system. To maintain operation, F-16s also incorporate specialized equipment for particular missions, such as electronic jamming devices (ECMs), firing devices, sensors,
but also, The airframe of 16 is now very old. In F-16V, There haven’t been any decreases in the radar cross-section, no use of stealth coatings, and no enhancements to the thrust of the F110 engine. Avionics are the only areas that have been upgraded, with new cockpit displays, electronic warfare and
AESA radar. However, there are no thrust-vectoring engines of any kind built into the F-16. Warfare systems and an integrated AESA radar. The F-16 Viper series can partially suppress current air defenses.
J-10C
The J-10c is an improved variant of the J-10B, it has a WS-10B engine, an infrared imaging seeker, and an indigenous Active electronically scanned array (AESA) fire-control radar.

One of the most capable light fighters is the J-10C. It has significantly improved with the incorporation of AESA radar, PL-10, PL-15, and the use of stealth coating.
The design uses modern innovations created in the 1970s to offer a top single-engine platform. The fighter was a little bit lighter than the F-16. Still, it performed better in flight, outperforming the American F110 in terms of power, speed, operational altitude, and maneuverability. Its airframe was a bit lighter despite having a more powerful engine, which further boosts its maneuverability advantage. Three-dimensional thrust vectoring systems give the WS-10B a significant maneuverability advantage. The J-10 also has the advantage of integrating an IRST, allowing it to lock onto stealth aircraft more easily at medium and short ranges. The J-10C’s benefits in weapons and flight performance are better.

The J-10C fighter is now regarded as the most advanced and potent model of China’s J-10 fighter aircraft. Beijing is confident that this aircraft is one of the most powerful fighters of the present generation. The creator is optimistic that the J-10C can compete with the US F-15E and the Russian SU-35. The J-10C fighter is essentially based on the J-10B model with supersonic diffuser air intakes (DSI) to address the central flaw of the J-10A version, allowing the J- 10 to run steadily at high speed even if it requires contemporary flight control software.
While the F-16 has a cropped delta wing arrangement without canards, the J-10 has a pure delta wing configuration. The J-10 is stable even at low speeds for ground attack because of its pure delta wing. Low-speed instability affects the F-16. As a result, the J-10 is superior to the F-16 regarding the ground assault. Still, the F-16 is superior to the J-10 in maneuverability due to its cropped delta wing layout. So, in a dogfight, the F-16 will prevail over the J-10. However, the F-16 is more jamming-capable and has a more powerful optoelectronic suite. As a result, the J-10 has more available thrust than the F-16, but Russian engines are less reliable than American engines.





